Endocrinology, a specialised branch of medicine, is concerned with the study of hormones and the diagnosis and treatment of hormone-related disorders. Hormones, the body’s chemical messengers, regulate a plethora of physiological processes, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction. This field encompasses a wide range of conditions, from diabetes to thyroid disorders, and involves both clinical practice and research. Within endocrinology, paediatric endocrinology focuses on hormone-related issues in children, addressing unique challenges in growth and development.
Paediatric endocrinologists are medical professionals who diagnose and treat hormonal imbalances in children. Their expertise is crucial for managing conditions that can significantly impact a child’s growth and development. Unlike adult endocrinology, paediatric endocrinology considers the dynamic changes occurring during childhood and adolescence, necessitating a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment.
In the UK, the prevalence of paediatric endocrine disorders necessitates a robust healthcare framework. For instance, around 35,000 children and young people in the UK have Type 1 diabetes, highlighting the need for specialised endocrine care. Furthermore, the UK has a proactive approach to screening for congenital hypothyroidism, ensuring early detection and treatment.
The influence of paediatric endocrinology extends beyond the immediate management of hormone disorders. Effective treatment can significantly improve the quality of life and long-term health outcomes for affected children. Early intervention and continuous management help mitigate the potential complications of endocrine disorders, enabling children to lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Moreover, advancements in research and treatment protocols continue to evolve, offering new hope for better management of paediatric endocrine conditions. Emerging therapies and innovative technologies, such as continuous glucose monitoring for diabetes and new growth hormone formulations, are enhancing care and outcomes.
Paediatric endocrinology plays a vital role in the health and development of children with hormone-related disorders. Through specialised care, paediatric endocrinologists address the unique challenges posed by these conditions, ensuring that children receive the necessary treatment to thrive. In the UK, the commitment to advancing paediatric endocrinology through research, education, and clinical excellence continues to make a significant difference in the lives of many children and their families.
Learn how we test and treat paediatric endocrinology at Paediatric Diagnostics.
A skin prick test, also known as a puncture or scratch test, is a common diagnostic tool used to identify allergic sensitivities. This simple, minimally invasive procedure involves introducing small amounts of potential allergens into the skin, typically on the forearm or back, to observe for any allergic reactions. It is widely used in paediatric medicine to diagnose allergies in children, helping to pinpoint specific allergens responsible for symptoms such as asthma, eczema, hay fever, and food allergies.
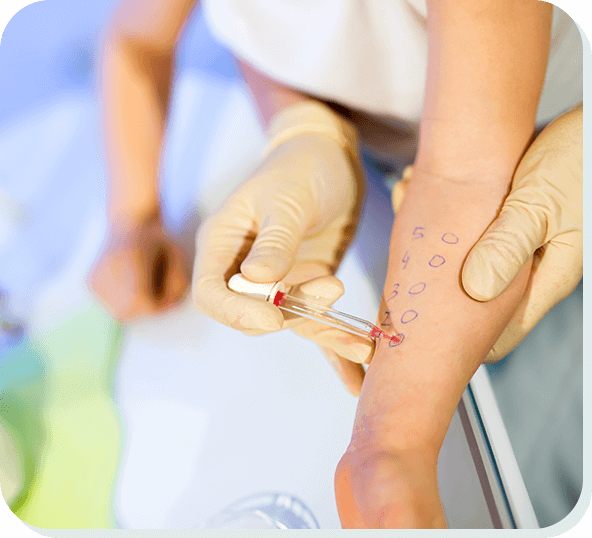
The primary purpose of a skin prick test is to determine whether a person is allergic to specific substances. These allergens can include:
In paediatric medicine, identifying these allergens is crucial for managing and mitigating allergic reactions, which can significantly impact a child's quality of life.
The skin prick test is performed in a controlled environment, usually in an allergy clinic or a specialist's office. Here’s what typically happens during the procedure:
In paediatric medicine, skin prick tests are essential for diagnosing allergies in children, who may present with a variety of symptoms that can be challenging to interpret. Allergies can manifest in numerous ways, including respiratory issues (like asthma), skin conditions (such as eczema), gastrointestinal problems, and anaphylaxis, which is a severe, potentially life-threatening reaction.
Early and accurate diagnosis of allergies through skin prick testing can lead to better management strategies. This might include allergen avoidance, medication to control symptoms, or immunotherapy to desensitise the child to specific allergens. For instance, identifying a child's allergy to peanuts can lead to crucial lifestyle changes and emergency preparedness measures, significantly reducing the risk of severe reactions.
Allergies are a growing concern in the UK, particularly among children. According to Allergy UK, approximately 5-8% of children in the UK have a proven food allergy, and allergic conditions are among the most common chronic disorders of childhood. The prevalence of eczema, asthma, and hay fever has increased significantly over the past few decades, affecting around 20% of children at some point.
Early testing and diagnosis are vital in paediatric allergy management. Skin prick tests are a key part of this process, providing rapid results that can guide further treatment and management plans. By identifying specific allergens early, healthcare providers can implement effective strategies to manage and mitigate allergic reactions, improving the overall health and well-being of the child.
A skin prick test is a valuable diagnostic tool in the field of paediatric medicine, helping to identify specific allergens that can cause a range of allergic reactions. In the UK, where the prevalence of allergies in children is significant, this test plays a crucial role in early diagnosis and management. By understanding what a skin prick test is and its importance, parents and caregivers can better navigate the complexities of allergies, ensuring that children receive the appropriate care and intervention to lead healthier, happier lives.
Book a skin prick allergy test at Paediatric Diagnostics today.
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux (GER), is a common condition in children where stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus, causing discomfort and potential complications. In the UK, it affects a significant number of infants and children, with estimates suggesting that up to 50% of babies experience reflux during their first few months of life.
The condition can manifest through symptoms such as frequent vomiting, irritability, and difficulty sleeping. While many children outgrow gastroesophageal reflux by their first birthday, ongoing symptoms can indicate gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which requires medical attention to manage and prevent further health issues.
Understanding and recognising the signs of acid reflux is crucial for parents and caregivers to ensure proper treatment and comfort for affected children.
Three main signs of acid reflux in children are:
Contact Paediatric Diagnostics today to book an initial consultation for your child.
Ultrasound imaging, commonly known as sonography, is a crucial diagnostic tool in pediatric medicine. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body, helping doctors diagnose and monitor various conditions in children without the need for invasive procedures or exposure to ionizing radiation.

In this article, we look into how ultrasound benefits paediatric care.
One of the biggest advantages of ultrasound in pediatric care is its safety. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, ultrasound does not use radiation, making it safer for children whose tissues and organs are more sensitive to radiation exposure. The non-invasive nature of ultrasound also means that it does not require any incisions or injections, which can be particularly advantageous for children who may be anxious or afraid of medical procedures.
Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, which is invaluable in paediatrics. This allows physicians to see the structure and movement of a child's internal organs and blood flowing through blood vessels in real-time. For infants and young children who cannot always communicate their symptoms or cooperate during an exam, ultrasound becomes an essential tool for quick and effective diagnosis.
Ultrasound is incredibly versatile and can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions in children, including but not limited to:
Ultrasound is also used to guide medical procedures in children, such as the placement of needles for biopsies or when draining fluids. This is important because it increases the accuracy and safety of these procedures, minimising the risk associated with more invasive techniques.
When compared to MRI and CT scans, ultrasound is often less costly and more accessible. This makes it an invaluable resource, particularly in urgent care settings or communities with minimal medical infrastructure.
Children, especially young ones, can find it difficult to stay still for long periods, which is necessary for many diagnostic tests. Ultrasound examinations are usually quicker and can be performed while the child is sitting or even lying in a parent's lap. This flexibility can help to reduce stress for both the child and the parents, leading to more accurate results and a more pleasant experience overall.
Ultrasound is indispensable in paediatric care due to its safety, versatility, and the detailed, real-time information it provides. It helps in the early diagnosis and treatment of various conditions, guiding procedures with greater accuracy and offering a more child-friendly approach to medical imaging. As technology advances, the role of ultrasound in paediatrics is likely to grow even more, helping to ensure better health outcomes for children around the world.
At Paediatric Diagnostics, we provide top-quality private paediatric ultrasound services for your child's medical needs. Our experienced team of specialists is committed to delivering exceptional care, using advanced imaging technology to accurately diagnose and monitor various conditions in children.
Endocrine disorders encompass a broad category of diseases that occur when the endocrine system, the network of glands that produce, store, and release hormones into the bloodstream, does not function properly. These hormones are vital for controlling a variety of bodily processes, including metabolism, mood, sleep, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, and reproduction. A disturbance in the hormone balance might result in serious health problems.

Endocrine disorders are often caused by various factors, including genetic mutations, diseases, infections, changes in the body's immune system, or damage to an endocrine gland. Some common conditions, like diabetes, occur when glands produce too much or too little of a hormone, known as hyperfunction and hypofunction. Other disorders, such as thyroid diseases, can arise from structural problems in the glands, including growths or tumours.
The symptoms of endocrine problems might vary depending on which hormone is implicated, but they frequently include changes in blood pressure or heart rate, exhaustion, increased thirst or urination, muscle weakness, mood swings, blurred vision, changes in appetite, and abnormalities in digestion. For instance, signs of hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid, can include weight gain, lethargy, and cold intolerance. In contrast, an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) might result in weight loss, increased heart rate, and anxiety.
The treatment for endocrine disorders depends on the specific disease and the underlying cause but typically focuses on restoring hormone balance. Common treatments include:
Effective management of endocrine disorders often requires a comprehensive approach, including regular monitoring of hormone levels, adherence to treatment plans, and adjustments to therapies as needed. Untreated endocrine abnormalities can result in major health complications because the endocrine system is essential to general health. Therefore, early detection and treatment are crucial.
In summary, endocrine disorders are a group of diseases resulting from the dysfunction of the glands in the endocrine system. They can have a variety of causes and symptoms, which can make diagnosis difficult at times. However, with proper treatment and management, many people with endocrine disorders can lead healthy, normal lives.
If you think that your child may be suffering from an endocrine related disorder, please contact Paediatric Diagnostics today to arrange an initial consultation.
Cows' milk protein allergy (CMPA) can present with a range of symptoms in children, affecting the skin , digestive, and respiratory systems. Look out for signs such as abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, eczema, blood or mucous in stools, constipation, severe gastro-oesophageal reflux, wheezing, and excessive fussiness after feeding.

CMPA occurs when a child's immune system reacts adversely to proteins found in cow's milk. The two main proteins responsible are casein and whey. The immune response triggers symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe reactions, making it crucial for parents to be aware of potential allergens in their child's diet.
The primary treatment for CMPA involves eliminating all sources of cows' milk protein from the child's diet. This includes breastfeeding mothers avoiding dairy or switching to hypoallergenic formulas. In severe cases, healthcare providers may prescribe specialised hypoallergenic formulas to ensure the child receives adequate nutrition.
If you notice persistent symptoms in your child that may be indicative of CMPA, it's important to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and management can significantly improve the child's quality of life. Immediate medical attention is crucial if there are severe symptoms like difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
Confirmation of CMPA often involves diagnostic investigations. These may include skin prick tests, blood tests measuring specific antibodies, or an oral food challenge under medical supervision. These tests help healthcare providers determine the severity of the allergy and guide appropriate treatment.
Preventing CMPA largely revolves around early detection and careful dietary management. If there is a family history of allergies, especially to cows' milk, it's advisable to monitor your child closely for any signs of allergic reactions. When introducing solids, gradually incorporate new foods, and be vigilant for any adverse reactions. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures associated with cows' milk protein allergy, parents can actively contribute to their child's well-being.
Regular communication with healthcare providers ensures a collaborative approach in managing CMPA and providing the best possible care for your child.
Contact Paediatric Diagnostics today.
A recent article by the Standard newspaper explained how Professor CK Sinha, Consultant Paediatric General and Urology Surgeon, and his team helped to save the life of a premature baby who was expected to die a few hours after being born when surgeons discovered she had a dead bowel.

Regarding the surgery, Professor Sinha said, “The surgery was a huge success, and we were so excited to see it happen, but it was also a challenging journey.
“We kept ourselves positive, and a huge credit needs to go to Connie’s parents, who were so supportive throughout. It was a whole team effort, and everyone was there to support Connie and her parents throughout their journey.”
Read the full article here: Doctors save life of baby with ‘miracle’ rare surgery at St George’s Hospital in south London.
Professor CK Sinha has over 25 years’ experience in paediatric surgery and paediatric urology, and is part of the team at Paediatric Diagnostics.
He has authored or contributed to over 115 publications, 15 books, and 50 national and international presentations. One of his most popular books is ‘Handbook of Paediatric Surgery’, published by Springer London – New York.
He is also the Clinical Governance Lead at St George’s Medical School and is actively involved in training the next generation.
To learn more about Professor CK Sinha, and the rest of our amazing team at Paediatric Diagnostics, please click here.
Neurodevelopmental disorders like Autism and ADHD can present with behavioural and educational difficulties, and diagnosing these conditions as early as possible can enable early treatment, which can have very encouraging results.
Late diagnosis carries an increased risk of developing mental health illnesses in adolescence and adulthood.
With this in mind, it is important to know the main symptoms of ADHD in children to look out for.
The main symptoms include:
According to research, boys are twice more likely to be diagnosed with ADHD when compared to girls, with the age of 7 being the most common time when children are diagnosed with the condition.
If you think that your child has ADHD, please get in touch with Paediatric Diagnostics today.
We provide Neurodevelopmental specialist assessments for children and young people up to 18 years old, and our team has extensive experience in dealing with neurodevelopmental disorders.
Paediatric Diagnostics can also offer in-depth evaluations of autism and ADHD. All our assessments and tools are in line with the current NHS guidelines.
Tongue-tie (ankyloglossia) is a common problem involving a band of skin between the underside of the tongue and the floor of the mouth. If this band of skin is very tight it can restrict the movement of a baby’s tongue making breastfeeding difficult.
Breastfeeding improves fast for some newborns following tongue-tie removal. Others may require many meals before seeing an improvement. Unfortunately, some newborns who have a tongue-tie division may not improve.
In a recent news article on the BBC, two mums told of the problems they have had when trying to feed their newborn babies with the condition.
Mother-of-two Clare Sinton saying that the experience was “Excruciating, unbearable, helpless.”, whilst Katharine Sharlott struggled to feed her newborn after a midwife said that his tongue movement looked fine, despite it turning out that her son had a 75% tie.
Read the full article here:
Tongue-tie: Mums and babies ‘let down’ by poor services
Tongue tie division can be performed by our paediatric ENT surgeon supported by one of our paediatric nurses. If your child is less than 3 months of age this can usually be carried out safely in our paediatric clinics. A tongue-tie assessment and division can be arranged for a total fee of £250.
Click here to learn more about tongue-tie division at Paediatric Diagnostics.



